+38 044 223 95 34 techno@alten-ua.com
Industrial automation.
The main function of industrial automation is to manage, control and save energy resources.
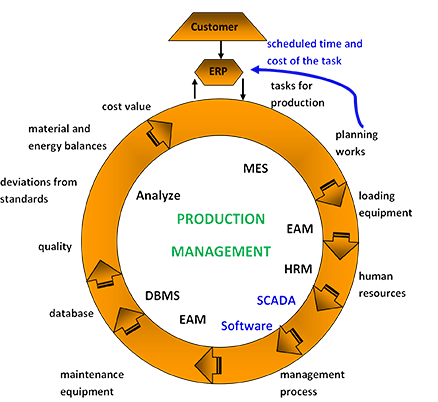
The components of industrial automation systems include: resource management systems (ERP); asset management systems (EAM); specialized information systems, SCADA systems (data acquisition and supervisory control systems), automation systems for local technical processes; controllers that perform control tasks and optimal management based on data from primary converters.
Order projects on techno@alten-ua.com and we will solve your tasks.SCADA — data acquisition and supervisory control systems visualize the technological process on mnemonic diagrams with active graphics that are understandable to a dispatcher familiar with the technological process and enable operational control of technological processes.
Applications Data acquisition and supervisory control systems
- housing and communal services;
- social sector facilities;
- agricultural complexes;
- food processing industry;
- energy sector;
- the mining industry;
- construction industry;
- transport;
- plants; factories
and many others.
Applications MES (manufacturing execution system) is a tool for increasing the profitability of the manufacturing business by:
- reduction of production costs; production losses
- reduction of energy consumption;
- improving the quality of products;
- reduction of the production cycle;
- improving the efficiency of management;
- increasing the information transparency of production:
MES applications enable:
describe the material and energy streams for all components and stages of processing; automatically calculate material and energy balances between any elements of the technological chain; analyze material and energy losses at any technological stage; create production tasks; automatically generate orders for materials and work orders for work and send them to contractors; to carry out network planning work for an unlimited period; to carry out product quality control based on a process approach that complies with the international ISO standard 9000:2000; calculate the cost of production in real time at each technological stage; to control the compliance of the time and cost of production tasks with the planned indicators; identify "bottlenecks" in production - the causes of cost growth, defects, losses, deviations from deadlines, etc; automatically generate reports and calculate indicators necessary for decision-making, etc.
EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) for the management of fixed assets, maintenance and repairs of a manufacturing enterprise allow:
- automate the accounting of fixed assets of the organization during their full life cycle;
- introduce modern methods of preventive and predictive maintenance, reduce equipment downtime;
- increase the productivity of the equipment;
- extend the service life and reduce operating costs;
EAM applications enable:
carry out equipment certification; develop EAM regulations for preventive and predictive maintenance; assign priorities for equipment maintenance; based on the EAM regulations automatically generate orders for materials and work orders for maintenance work and send them to contractors; carry out network planning of maintenance work for an unlimited period; to carry out control of the work; take into account the cost of materials and equipment maintenance; control the compliance of the time and cost of maintenance with the planned indicators; automatically generate reports and calculate indicators necessary for decision-making, etc.A specialized software exists for modeling and optimizing technological processes.
The implementation of a resource planning system makes it possible to achieve short payback periods from the implementation of automated management systems.
© LLC "ALTEN-TECHNO" 2014-2023